Only $99 for a full year!
No credit card required
Rank on Google's first page in 3 months
Canonical Tag: A Detailed Guide of Beginners
Dec 06, 2023 | prashant@growth.cx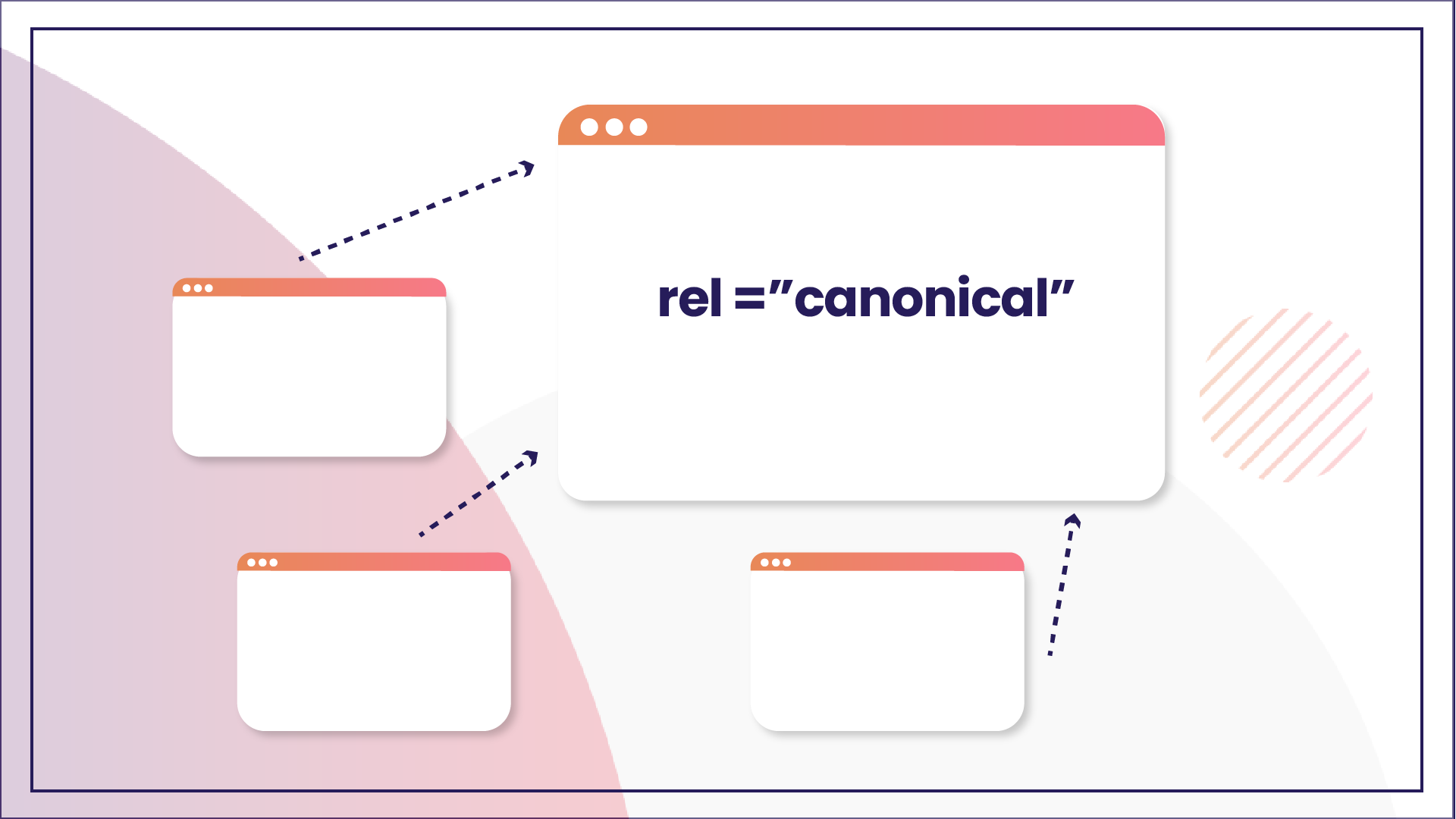
If you are new to the world of SEO and want to learn many ways to earn traffic through search engines then you will likely discover that getting your website listed as a Canonical Tag is one of the best ways. The reason it’s such a popular technique is because it gives Google an indication that the site has been verified by other websites in your niche. This triggers the ‘authority’ algorithm.
You’re probably already familiar with the latter because they’re a part of your website. In this article, we’ll take a look at what canonicals are, why they matter, and in what ways you can use them in your daily web design work.
What Are Canonical Tags?
Canonical tags, identified by the HTML attribute “rel=canonical,” are essential elements in web development and SEO.
You can use canonical tags to specify the main version if you have the same or similar content under different URLs. By indicating which URL is the authoritative source, search engines can prevent issues related to duplicate content and ensure more accurate indexing and ranking in search results.
This is how a canonical tag would look like:

Canonical tags are placed within the <head> section of a web page:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/sample-page/” />
Breaking down the code in simpler terms:
- link rel=”canonical”: This signifies the primary or canonical link.
- href=”https://example.com/sample-page/”: This points to the designated canonical version of the content, specifying the preferred URL.
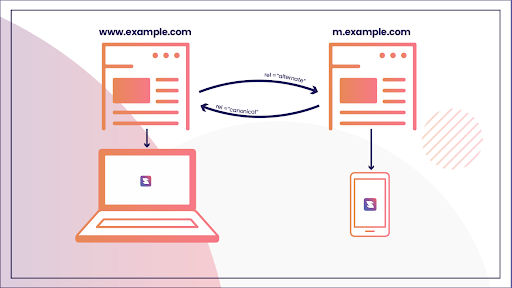
What Are Canonical URLs?
Canonical URLs are an essential part of your website. They are the URLs you will use in all your marketing materials, product descriptions, and other places.
They are essential because they help search engines understand what is on your site and how to get there. The Canonical URLs also help customers find what they need by providing a unique address that only you have.
[su_note note_color=”#dee9ec”]The canonical URL is the most commonly used URL for websites and can be used as a bookmark or bookmarklet. It’s the main website page, so if you create a new page, it will be automatically added to this list. You can see how this works on any website with multiple pages or posts – click on one link, then click again on another. If both links take you to different pages (or parts of the same page), those pages/posts aren’t considered canonical because they don’t match each other.[/su_note]
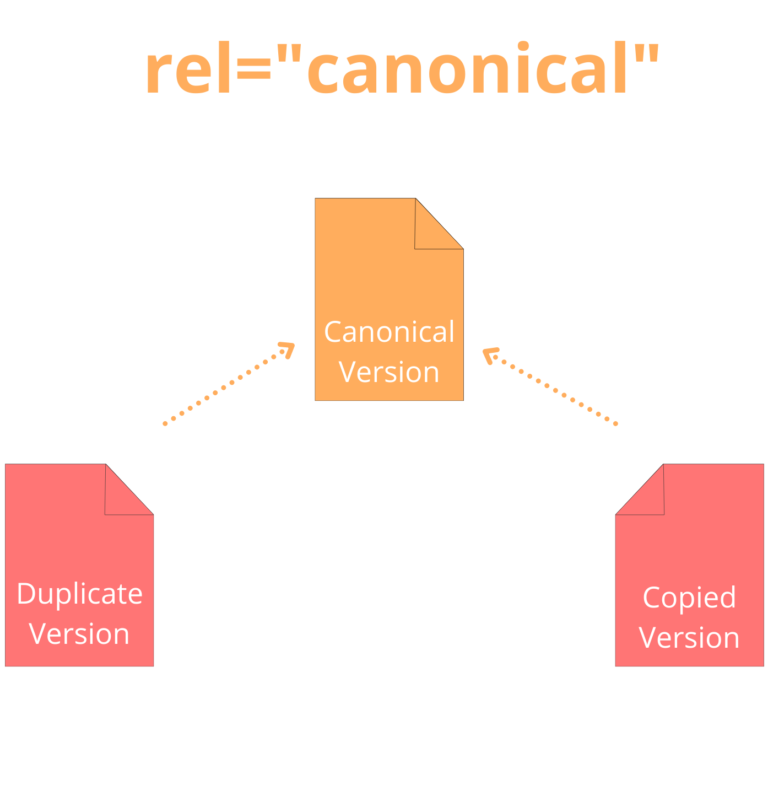
Duplicate content: Reasons why it exists
Duplicate content can be a problem for any website.
It is time-consuming and expensive to do, and challenging to track down. This is because the same information may appear on multiple pages and be referenced by different keywords in different places. Duplicate content is a problem for all businesses, especially those with high traffic to their site.
The issue arises when people visit your site and find duplicate content instead of the original page they were looking for. For example, if you have an FAQ page on your website and someone searches for “FAQ,” they may come across multiple pages with the same information as yours.
Another reason duplicate content exists is that it’s easy to confuse visitors when multiple websites have similar information about a topic. For example, when Google indexes your website and finds multiple pages with the same information about products or services you sell, it will display those pages at the top of their search results pages (SERPs). This could lead visitors looking for specific information about one product or service to end up on one of these duplicate pages instead of yours.
There are several reasons why duplicate content exists:
- An error in the original copy of a post or page was replicated across multiple locations.
- The absence of a clear editorial strategy.
- A post or page was republished from an external source without proper credit.
- A blog post or page has been copied without proper attribution, resulting in multiple versions of the same piece of content appearing on your site or blog.
- The original author didn’t add a meta description tag for critical keywords, making it difficult for people searching for information about that topic on Google to find you!
- The Internet is a global network that connects people across borders and cultures. As such, there are certain rules that different countries have when it comes to publishing online content that infringes on copyright laws. Certain countries have stricter regulations than others when it comes to how much or how little content is allowed on the web — this means duplicate content will happen more often in some countries than others!
- A website may have been updated with new content, but the old version is still indexed by search engines, so people will still see it when they search for an old keyword or phrase.
Why Canonical Tags Are Important for SEO
The canonical tag is an essential element of SEO because it tells search engines how to prioritize your content. This is why canonical tags are among the most critical factors in search engine rankings.
When you have a website or blog with multiple pages, each of which can be accessed via a different URL, you need to make sure that you set up the correct canonical tag for each page. This is done by creating a unique HTML code that tells search engines which version of your content is the most important (that’s what the “canonical” part means).
A canonical tag is a link to a specific URL on your site. This can help prevent duplicate content, as well as improve user experience.
One example is if you have a page on your site with multiple versions, such as an About Us page with multiple pages linked to it. If you set up a canonical tag for each version, Google will display all of them in search results when users search for “about us.”
Another use case will be if there are multiple pages on your site with similar content but with different URLs or titles. You could set up canonical tags for each page so that when users search for something like “about us,” Google displays all versions of that page at once.
Here’s a tip: You know how vital canonical tags are for SEO, right? Monitor them using a technical SEO tool and adjust to maximize their effectiveness.
How to Implement Canonical Tags?
To implement canonicals, you need to have a list of URLs you want to be treated as canonical. It’s essential to have this list organized in a way that makes sense for your site, and it should include all the different ways people can get to your content:
[su_note note_color=”#dee9ec”]The canonical tag is the most common way to indicate that a given URL is the preferred one (so it should be used if possible). The canonical tag has the format, where URL-to-original is the URL of the page that you want to treat as the “master page”.[/su_note]
You can also use robots.txt to tell search engines where they should go. This is particularly useful if your site has multiple subdomains with multiple versions of content on each subdomain (which happens quite often).
The best practice is to use a canonical tag on every homepage of your site and always include it in the <head> section of the HTML code. This ensures that search engines can correctly interpret the information on your website’s content pages.
You must also not use duplicate content in your SEO strategy if multiple URLs point to one page. They may not be considered separate pages by Googlebot.
How to add a Canonical tag in WordPress?
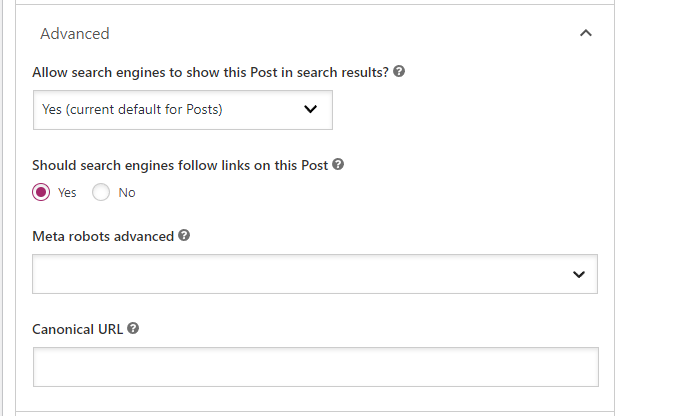
WordPress is a popular CMS and blogging platform. Millions of bloggers around the world use it. In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to add Canonical Tag in WordPress with the help of a plugin.
- Install WP Canonical Tag or any SEO Plugin
- Activate the plugin
- Add a canonical tag in your post or page in the editor window
Here is another way you can add a canonical tag in WordPress without a plugin:
Step 1: Go to Settings > Permalinks from the Admin dashboard and then click on Permalink Settings.
Step 2: In the Permalink Settings window, scroll down to the bottom and enter your custom permalinks for your site.
Step 3: Click on the Save Changes button at the top right corner of your screen when done with editing your permalinks settings.
How to add a Canonical tag in HTML?
This is a simple and easy way to add the canonical tag to your HTML page.
Add the following code at the end of your HTML file:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/">It is essential to use this tag as it can help search engines to crawl your site correctly. Adding this tag will tell search engines that you want your page to be crawled as a single entity and not separately for each version. Search engines like Google will then crawl all the pages in one go, thus improving their chances of finding out information related to your website.
Canonical Tag Best Practices
Regarding SEO, the Canonical Tag is a crucial component of your webpage’s content. This is because it will help search engines understand the overall structure of your website and make better-informed decisions about indexing and ranking your site.
Below are some best practices to follow when creating canonical tags:
i. Include a Slug in the Canonical Tag
Include a word or short phrase before each slash (/) in the canonical tag. This helps search engines understand what pages on your website are related to each other, allowing them to understand their relationship with other sites better.
ii. Don’t Duplicate Tags for Different Pages or Categories
You should only have one canonical tag per page or category so that search engines can adequately identify which URLs are relevant to each other.
iii. Use Only Canonical URLs in Your Sitemaps.
Only put the primary URLs in your sitemap. Don’t add any other URLs that aren’t the main ones. Google thinks the sitemap URLs are the main versions of your web pages. Stick to this rule to ensure search engines get the right idea about your site.
iv. Self-Referencing Canonicals
Pages are not required to use canonical tags, but it doesn’t hurt to do so. Canonical tags that link to themselves are called self-referencing canonicals. For instance, when https://www.example.com/page1 contains this canonical tag:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/page1”>
It doesn’t hurt to do so, even if you do not have to. It may seem obvious on the surface, but most SEOs face this question.
v. Ensure That Your Canonical URL Can Be Accessed
I’m sure you already know this.
Can you explain why a page is claimed to be the definitive version, but Google is redirected to another URL? Is it to redirect Google to a 404 page? Is it to redirect to a URL that has been blocked by robots.txt? That happens sometimes.
Canonicalize only URLs allowed in your robots.txt file and return a 200 status code. Verify noindex tags on canonical URLs.
Use a program that generates canonical tags dynamically to double-check them. Some CMS platforms and plugins use self-referencing canonicals for every URL published on your site, which defeats the purpose of URL canonicalization.
vi. Use Absolute URLs
Include the full URL when adding a canonical tag. The URL must contain the following elements:
- The HTTPS://
- Your domain name
- The www (if it’s part of your preferred domain)
- The .com part.
“Relative URLs” only include the part following “.com,” and Google does not recognize them when it looks at your canonical tags.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing Canonical Tags
1. Duplicate tags
This is one of the most common mistakes which can cause your site to be penalized by Google. If you have duplicate tags, then it means that your pages are not following the same structure and layout.
For example, if you have a blog post on your website and three different categories, then there is no point in having a canonical tag for each category. Instead, you should add a single canonical tag for the page itself.
2. Missing <link> tag
This mistake may lead to duplicate content being indexed on Google’s search engine results page (SERPs). If you don’t include a <link> tag in your HTML code, then Google will think this page has been published more than once on the internet.
This will result in duplicate content indexing on Google’s search engine results page (SERPs).
3. Incorrectly implemented Cite Tag Meta Description
The meta description tag describes the contents of a particular web page or article in detail to help users understand its purpose and value within a niche market or industry.
The following are other common mistakes made when implementing canonical tags:
- Using non-canonical tags in the HTML <head> section
- Including non-canonical tags in the page <title> tag
- Not adding a canonical tag to all pages
- Not using the HTTP:// or HTTPS:// scheme in the canonical tag
Final thoughts
This is a fundamental guide to canonical tags and canonical links. If you have never heard of them before, this is the perfect article, to begin with. This explanation will make clear exactly what ‘canonical’ and ‘tag’ are and how they are used.
Canonical tags help us consolidate the distribution of multiple pages into one. Thus we can avoid problems with search engines and user experience. If you’re wondering how they work and if they’re suitable for your site, hopefully, this article will help you decide.
FAQ
1. What is a canonical tag?
It is an HTML element used for indicating the preferred version of a webpage when the same or similar content appears on more than one URL. It helps search engines understand which pages should be prioritized for indexing and avoids duplicate content.
2. What is a canonical link in SEO?
In SEO, a canonical link refers to the HTML link element (\<link rel=”canonical”…\>) that establishes the preferred or canonical URL for a specific webpage. It signals search engines to index URLs, addressing duplicate content concerns.
3. How to add canonical tags in HTML
To add a canonical tag in HTML, insert the following code within the \<head\> section of your webpage:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”your-preferred-url”>
Replace “your-preferred-url” with the URL you want to designate as canonical.
4. How to add a canonical tag to WordPress?
WordPress simplifies canonical tags. Use plugins like Yoast SEO or manually add the tag to your theme files. With Yoast SEO, go to the post/page editor, scroll down to the Yoast SEO section, and enter the canonical URL in the Canonical URL field.
5. Why do we use canonical tags?
Canonical tags are crucial to prevent duplicate content and multiple URLs leading to the same or similar information. By specifying the canonical version, you guide search engines to the preferred URL to index, improving search results accuracy and enhancing overall SEO.
